Sarcoidosis is a systemic inflammatory granulomatous disease that can affect any organ system. It can be mild or severe, depending on what is affected.
Sarcoidosis
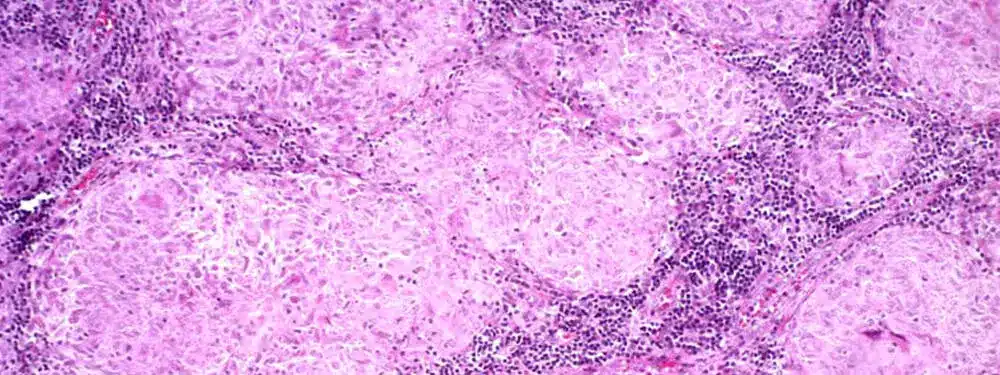
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is characterized by abnormal masses or nodules called granulomas consisting of inflamed tissues that form in any organ of the body. Symptoms depend on what body part is affected. It can manifest as lung nodules, inflammatory arthritis, nodular skin rash, uveitis, just to name a few. Sarcoid can be mild and flare up periodically, then go into remission. In some fortunate patients it can permanently go into remission. Treatment is tailored based on what body part is actively inflamed and symptomatic, and the decision is based on how mild or how severe the symptoms are. No treatment is needed for asymptomatic individuals.
How does Lomibao Rheumatology & Wellness Care treat Sarcoidosis?
The rheumatologist frequently co-manages sarcoidosis with other specialists depending on what organ is affected. If the sarcoidosis is severe and not responding to milder oral or injection treatment, then infusion such as Remicade (infliximab) may be needed.

