A severely painful version of arthritis, crystalline arthritis is caused by sharp crystals precipitating in joints such as the toes, knees or elbows. The crystals are a result of problems absorbing or breaking down various natural substances and create a painful inflammation and swelling in the joint itself. The most common types of crystalline arthritis include:
Crystalline Arthritis
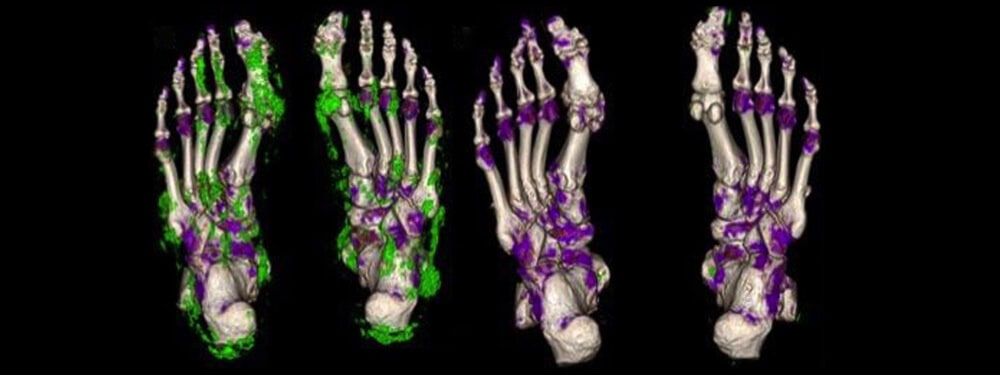
Gout
Gout is commonly characterized by sudden onset of severe pain, swelling and redness in the affected joints, frequently the big toe. It is caused by excess uric acid in the bloodstream. The symptoms often begin quite suddenly and if gout remains uncontrolled it can cause permanent joint damage and limit the normal movement of the affected joints, making everyday activities extremely painful. The definitive way to diagnose gout is to drain fluid from the affected joint and analyze it for uric acid crystals under a microscope. This is often not practical however if it is a small joint affected or multiple joints. In addition to medication, diet and lifestyle changes are very important in reducing the risk of recurrent gout.
Chronic CPPD Arthropathy
Chronic CPPD (calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease) arthropathy refers to when calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit all over multiple joints and cause multiple joint damage and chronic arthritis, presenting similarly to rheumatoid arthritis rather than episodic single joint pain such as pseudogout. X-rays will show calcium deposits in the joints. When clinically appropriate, it is prudent to rule out possible secondary metabolic causes of CPPD. There are currently no known treatments that exist for breaking down the crystals or preventing their formation, more research is needed. Treatment is aimed at reducing pain and swelling and preventing further joint damage, so the strategy is to treat these patients similarly to someone who has RA, when indicated.
Pseudogout
This condition presents similarly to gout but instead is caused by another substance called calcium pyrophosphate. Calcium pyrophosphate crystals deposit in the joints rather than uric acid. Pseudogout causes almost identical symptoms such as sudden and painful swelling in one or more joints, the most common being the knee although the wrists and hands can be involved as well. It is common in both men and postmenopausal women but does tend to affect people over sixty with more frequency. Definitive diagnosis is typically done by analyzing aspirated fluid from inflamed joints.
How does Lomibao Rheumatology & Wellness Care treat Crystalline Arthritis?
Acute symptoms of a flare-up are treated with fast-acting treatments such as oral and injection steroids, NSAIDs, and colchicine. For gout, uric acid-lowering medications such as allopurinol are needed for maintenance treatment and prevention of recurrent flare-ups. Diet and lifestyle modalities are especially important for preventing recurrent gout, including maintaining healthy body weight, and reducing purine-rich foods such as alcohol, soft drinks, shellfish and organ meats. If an underlying secondary metabolic cause is identified for CPPD, it should be addressed and treated accordingly. Chronic CPPD arthropathy that is unresponsive to initial treatment with steroids, NSAIDs, and colchicine may need treatment with DMARDs traditionally used to treat RA. Wellness services for crystalline arthritis – coming soon!

