This article will explore systemic autoimmune diseases, symptoms that could suggest an autoimmune condition is present, and the methods used for diagnosis. Abnormalities in immune system signaling play a key role in causing autoimmune conditions, consequently, innovative treatments seek to target these signals. By understanding the fundamentals of autoimmune diseases, individuals can live healthier lives, empowered with the knowledge about symptoms, treatment options, and latest diagnostic methods.
Types of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases
Systemic autoimmune diseases can involve multiple organs and tissues. Autoantibody formation is frequently the cause of these conditions. Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus are examples of autoimmune conditions.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by the immune system attacking the synovium, the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Rheumatoid arthritis commonly involves the finger and wrist joints. This condition can progress to severe joint damage and deformity if untreated. In rare circumstances, inflammation can occur outside of the joints in areas such as the lung, skin, and nervous system.

Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory arthritis that can commonly be associated with psoriasis, a skin disorder. Psoriasis looks like red or gray scaly patches of itchy skin. This type of arthritis can also progress to severe joint damage and deformity if untreated. Psoriatic arthritis can be associated with metabolic syndrome, meaning those prone to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and overweight and obesity.
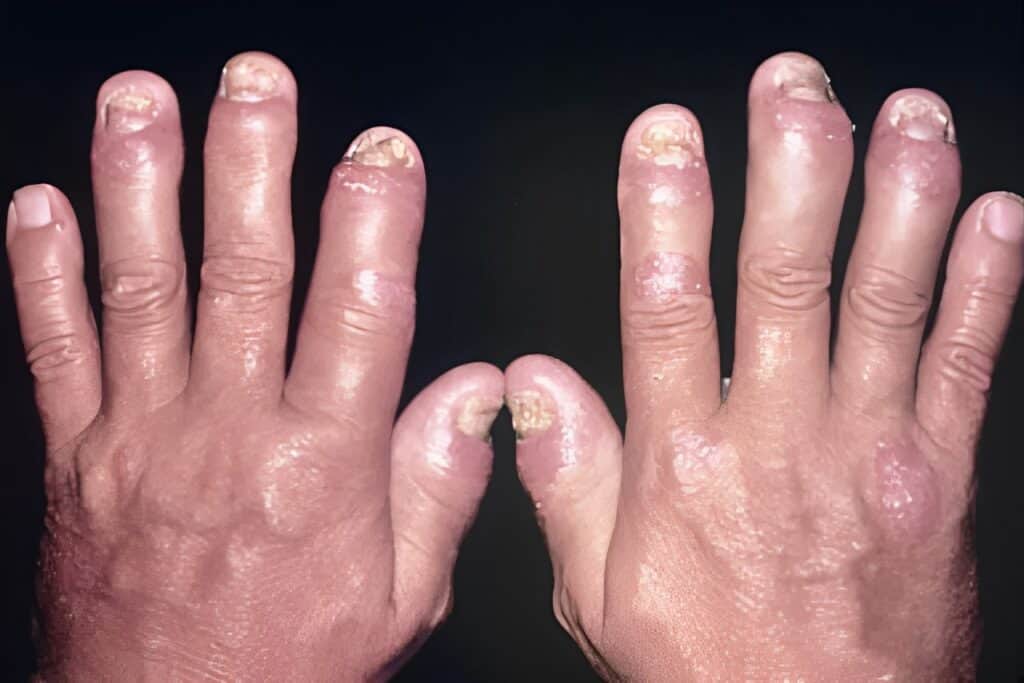
Lupus
Lupus, officially known as systemic lupus erythematosus, can look different in different people. Some symptoms are fatigue, joint pain, and rash. Lupus can flare up and go into remission. In some cases lupus can lead to serious complications such as kidney disease.
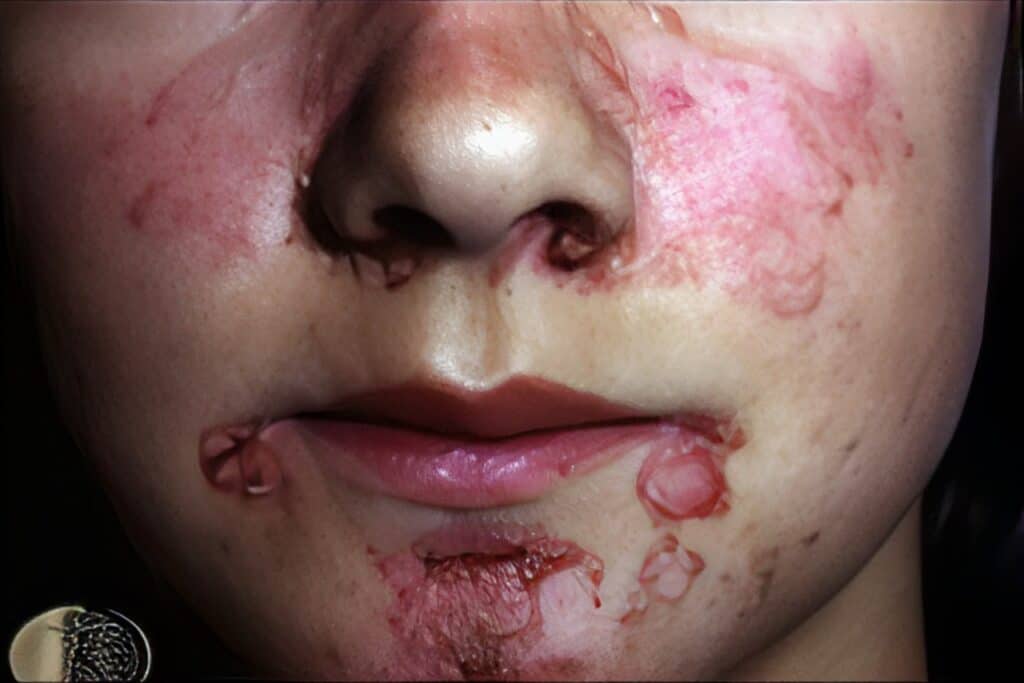
Common Symptoms
Many autoimmune diseases share common symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and rash, which significantly impact patients’ daily lives and overall well-being.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a common symptom in many autoimmune diseases. There is extreme tiredness that makes it hard to do everyday activities. Unlike normal tiredness, this fatigue doesn’t go away with rest and can seriously affect both physical and mental health. The fatigue is due to your own body fighting against itself.

Joint Pain
Joint pain is another common symptom. Individuals will have stiffness, swelling, and pain in joints. Joint stiffness in the morning is characteristic of inflammatory arthritis. Managing this pain effectively is crucial for maintaining mobility and reducing the overall burden of the disease.
Rash
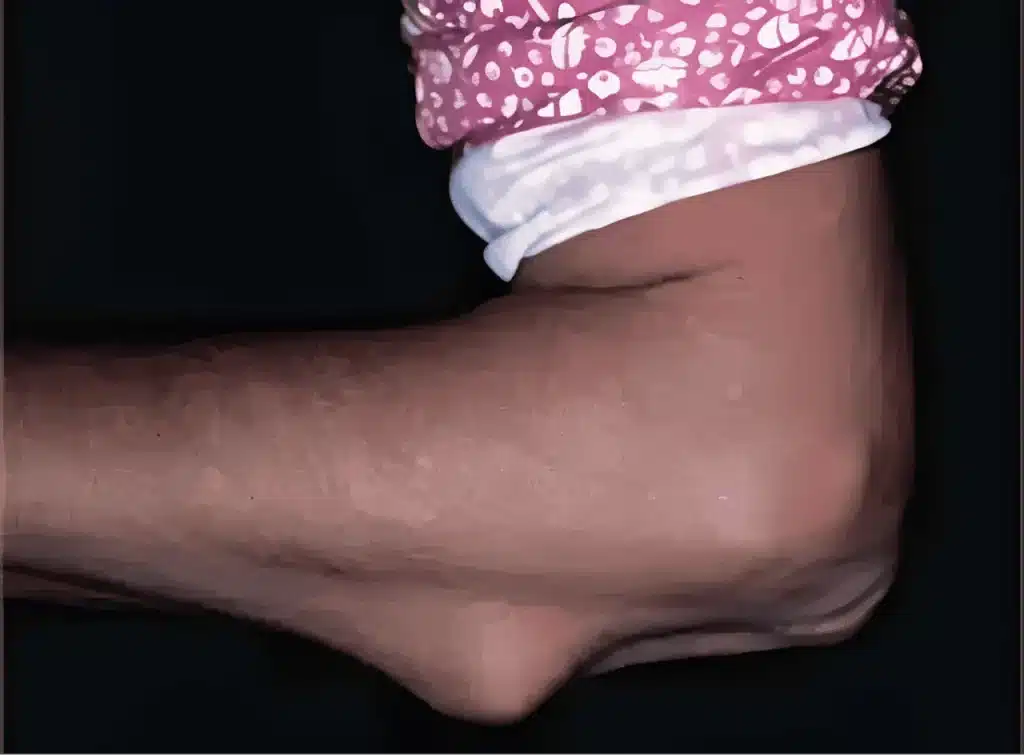
Autoimmune diseases can show up as skin symptoms. Conditions like lupus and dermatomyositis can have reddish or purplish rash triggered by sunlight. Psoriasis can have scaly patches worsened by stress. Rheumatoid nodules can occur on the elbows or back of the hands. The way these rashes look can help doctors diagnose the disease and track its progress.
Diagnostic Methods
There are several diagnostic methods used to identify autoimmune diseases, including blood tests and imaging techniques.
Blood Tests
Evaluation for autoimmune diseases often starts with blood tests, which are important for looking for clues such as abnormal inflammation markers and autoantibodies. Tests such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) give clues that there is general inflammation in the body. An abnormal Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) test can suggest that there is a potential immune reaction happening in the body. The rheumatologist will investigate disease-specific immune blood tests, called autoantibodies, to assist in pointing toward a specific condition. Blood tests such as Rheumatoid Factor (RF) and Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) are informative in identifying rheumatoid arthritis, and Anti-double stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) for lupus.
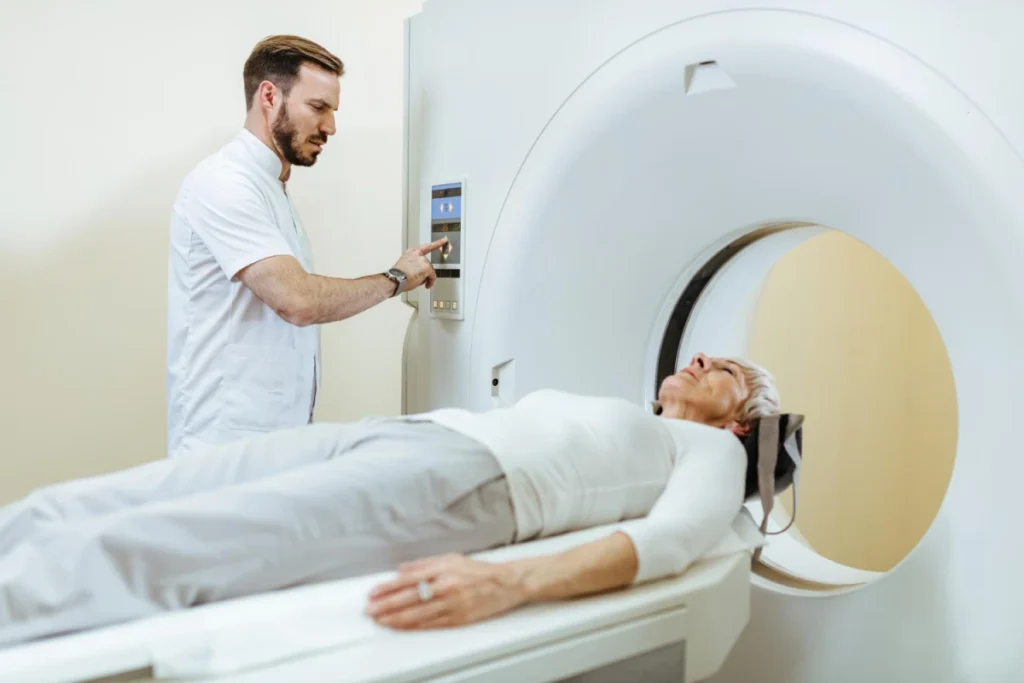
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques can be helpful in diagnosing and managing inflammatory arthritis. X-rays of joints can help find the diagnosis and determine if a treatment is working or not working. MRI can be useful to confirm if back pain is due to ankylosing spondylitis.
Conclusion
Systemic autoimmune diseases are challenging to diagnose and treat due to the diversity of how they can present in each individual. Recognizing symptoms that could suggest an autoimmune condition such as joint pain, fatigue, and rash can lead to earlier evaluation by a rheumatologist. Staying updated on the latest developments is important for patients and clinicians, as continued research will hopefully lead to a cure.
Lomibao Rheumatology & Wellness Care, led by Dr. Frances Lomibao, specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases and autoimmune conditions. Located in Rowlett, Texas, our clinic offers personalized care for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriatic arthritis using the latest medical technology. We are dedicated to improving patients’ quality of life through compassionate care and advanced medical expertise. For more information, visit www.lomibaorheumatology.com.